Introducing Blockchain, the Invisible Technology That Will Change the World of Business
Abstract
Blockchain is a new technology that is finding its way into the business world. It is not a company or an app, but rather a shared database that continuously updates itself and validates every block added to the linear chain.
Its perceived complexity has made it an anomaly in the world outside of technology, but its potential uses and benefits are undeniable. It’s already being used in the realm of business to create smart contracts, and other applications are coming to fruition as well. However, these opportunities also come with numerous distinct issues.
1. Introduction to Blockchain
To most of the world, blockchain is an elusive and daunting technology. Then again, so was the World Wide Web when it first launched in 1991. The tech itself may be hard to grasp, but many of its uses are not.
Blockchain technology presents a wide variety of business applications, as well as challenges to overcome. It is important to remember that blockchain is still in its infancy, and while the technology may seem trivial and easy to ignore now, it won’t be disappearing anytime soon.
2. Background
Blockchain’s most common association is with Bitcoin, the decade-old electronic cash system invented by someone under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin eliminated the need for an intermediary, such as a bank, in order to make a financial transaction. While Bitcoin has its own reputation and issues, the technology behind it, called blockchain, is a separate revolutionary electronic system.
Blockchain is a reliable and decentralized infrastructure that can store any digital asset, either for public or private use. Internet users can create value and authenticate digital information with the touch of a button.
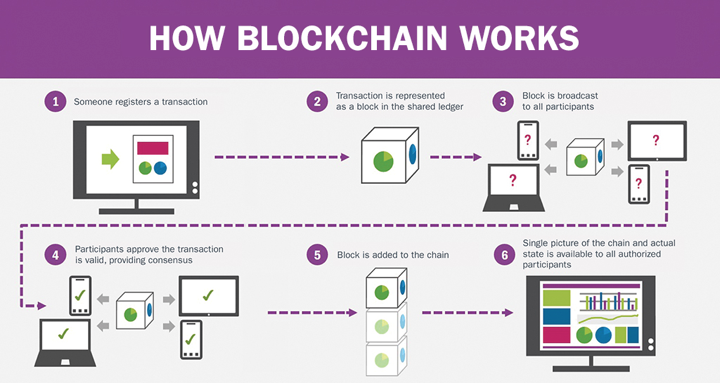
Source: MRONetwork.com
Blockchain technology can simplify small tasks, such as file storage and data management, as well as more complicated ventures including crowdfunding, supply chain auditing, and smart contracts.
3. Challenges
As it currently functions, blockchain can have an enormous environmental cost, which in turn will affect the businesses using it. The technology requires each computer in the network to solve a complicated cryptographic problem in order to keep the blockchain updated. This process requires massive amounts of computing power.
In 2017, the energy used to create the computing power that kept Bitcoin running was equivalent to the energy consumed by 159 of the world’s nations. While most blockchains won’t be nearly the size of Bitcoin, it is a crucial issue to consider as the technology grows in popularity.
As of today, the biggest challenge blockchain presents to businesses is its complexity. It is a misunderstood technology that cannot reach its full potential without an image overhaul. The tech itself may be incredibly complicated, but that doesn’t mean it’s difficult to use. However, without some research, it can be difficult to understand its benefits and overall importance. For blockchain to become a universal business tool, everyday people will require a more concrete understanding of its potential.
4. Opportunities
By utilizing blockchain, businesses that produce complicated products will be able to enjoy the enormous benefit of streamlining the management of multiple vendors involved in the production.
Supply chains can be convoluted and nuanced, which makes accountability challenging. Blockchain will create transparency by sharing data across every computer in the network, much like a decentralized, continually-updated ledger. The manufacturer will be able to trace the route of a specific product and identify every single step of the production process. So, if an issue arises, it can be reconciled immediately.
For example, in the case of Chipotle’s E. coli outbreak in 2015, blockchain would have been essential to pinpointing the source of the bacteria. Chipotle could have immediately cut off deliveries from that vendor before the bacteria had the chance to spread.
Along with simplifying processes, blockchain will lower the uncertainties involved in working with unfamiliar people or businesses. Each computer in the network does not need to know or trust any of the others because they all can monitor and validate the chain themselves.
Lastly, blockchains will provide businesses with impenetrable security. There are two types of blockchain networks: public and private. The two have a lot in common, however, public networks can be viewed by anyone on the Internet and private ones cannot. Private blockchains function like company intranets with data encryption to limit who can access the secure network. Confidential files will stay confidential, no matter what.
5. Conclusion
Blockchain is slowly creeping its way into the consciousness of the business world. Even with its challenges, the advantages and opportunities are innumerable. In fact, a smart contract public blockchain, called Ethereum, already exists. The platform may be young, but it is growing. Ethereum is proof that blockchain has real-world applications outside of financial services.
This technology may not be perfect just yet, but it is powerful and has the potential to revolutionize the world of business.
6. Citations
A Next-Generation Smart Contract and Decentralized Application Platform. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/White-Paper#ethereum
Canaday, H. (n.d.). Blockchain In MRO Could Happen Sooner Than You Think. Retrieved from http://www.mro-network.com/big-data/blockchain-mro-could-happen-sooner-you-think
Ethereum: Blockchain App Platform. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://ethereum.org/
Etwaru, R. (2017). Blockchain: Massively Simplified [Video file]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k53LUZxUF50
Jayachandran, P. (2017, May). The Difference Between Public and Private Blockchain. Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/blogs/blockchain/2017/05/the-difference-between-public-and-private-blockchain/
Nakamoto, S. (n.d.). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
Osborne, C. (2017). How blockchain can transform the manufacturing industry. Retrieved from https://www.zdnet.com/article/how-blockchain-can-transform-the-manufacturing-industry/
Warburg, B. (2016) How the Blockchain Will Radically Transform the Economy [Video file]. Retrieved from https://www.ted.com/talks/bettina_warburg_how_the_blockchain_will_radically_transform_the_economy#t-879931
What is Blockchain Technology? A Step-by-Step Guide For Beginners. (2016). Retrieved from https://blockgeeks.com/guides/...
